




















MOLCAS manual: Next: 8.6 chcc Up: 8. Programs Previous: 8.4 casvb
CCSDT performs the iterative single determinant CCSD procedure for
open shell systems and the noniterative triple contribution calculation to
the CCSD energy.
For further details the reader is referred to the
sections 6.14 and
|
| File | Contents |
| RSTART | file with CC amplitudes and CC energy.
The name of the file can be changed using keyword RESTART.
It contains restart information, like
T1aa,T1bb,T2aaaa,T2bbbb,T2abab, CC energy and the number of iterations.
|
| T3hfxyy | These files contain integrals of
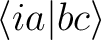 type where x
represents
the symmetry and yy the value of the given index i.
The number of
these files is equal to the number of type where x
represents
the symmetry and yy the value of the given index i.
The number of
these files is equal to the number of  occupied orbitals
( inactive + active. ) occupied orbitals
( inactive + active. )
|
8.5.3 Input
The input for each module is preceded by its name like:
&CCSDT
| Keyword | Meaning |
| TITLe | This keyword should be followed by precisely one title line. It should not begin with a blank (else it will not be printed!) This keyword is optional. |
| CCSD | This keyword specifies that only CCSD calculation will follow and the integrals will be prepared for the CCSD procedure only. This keyword is optional. (Default=OFF) |
| CCT | This keyword specifies that after CCSD calculation also noniterative T3 step will follow. For such calculations this key must be switched on. The integrals for the triple contribution calculation will then be prepared. This keyword is optional. (Default=ON) |
| ADAPtation | The parameter on the following line defines the type of spin adaptations
of CCSD amplitudes.
0 - no spin adaptation - full spinorbital formalism 1 - T2 DDVV spin adaptation 2 - T2 DDVV + T1 DV spin adaptation (only recommended for specific purposes, since the adaptation of T1 included incompletely) 3 - full T2 and T1 spin adaptation (in current implementations limited to doublets only) 4 - full T2 adaptation without SDVS coupling (for doublets only) This keyword is optional. (Default=0) |
| DENOminators | The parameter on the following line specifies the type of denominators that
will be used in the CCSD procedure.
0 - diagonal Fock matrix elements (different for 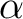 and and 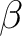 spins)
spins)
1 - spin averaged diagonal Fock matrix elements - 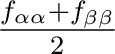
2 - orbital energies In some cases alternatives 1 and 2 are identical. For nonadapted CCSD calculations the resulting CCSD energy is invariant with respect to the selection of denominators. However, convergence may be affected. In the present implementation a symmetric denominators (i.e. the input 1 or 2) should be used for spin adapted CCSD calculations. This keyword is optional. (Default=0) |
| SHIFts | Following line contains socc and svirt levelshift values for occupied and
virtual orbitals respectively. Typical values are in the range 0.0 - 0.5 (in a.u.)
dp(occ)=dp(occ)-socc dp(virt)=dp(virt)+svirt For spin adaptations 3 and 4 only inactive (D) and active (V) orbitals will be shifted, due to the character of the adaptation scheme. For other cases all orbitals are shifted. This keyword is optional. (Defaults: socc=0.0, svirt=0.0) |
| TRIPles | The parameter on the following line specifies the
type of noniterative triples
procedure. There are three different types of perturbative triples available
(see Section ![[*]](crossref.png) ). ).
0 - CCSD approach (no triples step) 1 - CCSD+T(CCSD) according to Urban et. al [40] 2 - CCSD(T) according to Raghavachari et. al. [41] 3 - CCSD(T) according e.g. to Watts et. al. [16] This keyword is optional. (Default=3) |
| T3DEnominators | The parameter on the following line specifies the type of denominators that
will be used in noniterative triples procedure.
0 - diagonal Fock matrix elements (different for 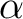 and and 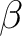 spins)
spins)
1 - spin averaged diagonal Fock matrix elements - 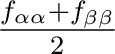
2 - orbital energies In some cases alternatives 1 and 2 are identical. This keyword is optional. (Default=0) |
| T3SHifts | The following line contains socc and svirt levelshift values for
occupied and virtual orbitals respectively.
Typical values are in the range 0.0 - 0.5 (in a.u.)
dp(occ)=dp(occ)-socc dp(virt)=dp(virt)+svirt In contrast to the iterative CCSD procedure, in noniterative T3 step results are not invariant with respect to the denominator shifting. It is extremely dangerous to use any other than 0.0 0.0 shifts here, since resulting T3 energy may have no physical meaning. This keyword may be useful only in estimating some trends in resulting energy, however, using of default values is strongly recommended. This keyword is optional. (Defaults: socc=0.0, svirt=0.0) |
| ITERations | This keyword is followed on the next line by the maximum number of iterations in the CCSD procedure. In the case of the RESTART run this is the number of last allowed iteration, since counting of iterations in RESTART run starts from the value taken from the RSTART file. This keyword is optional. (Default=30) |
| ACCUracy | The real value on the following line defines the convergence criterion on CCSD energy. This keyword is optional. (Default=1.0d-7) |
| END of input | This keyword indicates that there is no more input to be read. This keyword is optional. |
| EXTRapolation | This keyword switches on the DIIS extrapolation. This keyword is followed
by two additional parameters on the next line n1 and n2.
n1 - specifies the first iteration, in which DIIS extrapolation procedure will start for the first time. This value must not be less then n2, recommended value is 5-7. n2 - specifies the size of the DIIS procedure, i.e. the number of previous CCSD steps which will be used for new prediction. In the present implementation n2 is limited to 2-4. This keyword is optional. (Default=OFF) |
| The parameter on the next line specifies the level of output printing
0 - minimal level of printing 1 - medium level of printing 2 - full output printing (useful for debugging purposes) This keyword is optional. (Default=0) | |
| LOAD | This keyword is followed by the line which specifies the name of the CCSD amplitudes and energy file. The default name is RSTART, but it can be changed in CCSD step using RESTART keyword. This keyword is optional. (Default=RSTART) |
| RESTart | This keyword defines the restart conditions and modifies the name of the file,
in which restart information (CC amplitudes, CC energy and the number
of iterations) is saved. On the following two lines there
are control key nn and the name of restart information storing file
name.
nn - restart status key 0 - restart informations will be not saved 1 - restart informations will be saved after each iteration in name. 2 - restart run. CC amplitudes and energy will be taken from name file and the CCSD procedure will continue with these values as an estimate. name - specifies the restart information storing key. The name is limited to 6 characters. This keyword is optional. (Defaults: nn=1, name=RSTART) |
| IOKEy | This keyword specifies the input-output file handling.
1 - Internal Fortran file handling 2 - MOLCAS DA file handling The default (1) is recommended in majority of cases, since when calculating relatively large systems with low symmetry, the size of some intermediate files produced may become large, what could cause some troubles on 32-bit machines (2 GB file size limit). |
| MACHinetyp | This keyword specifies which type of matrix multiplication is preferred on a given
machine. The following line contains two parameters nn,limit.
nn =1 standard multiplication A x B is preferred nn =2 transposed multiplication AT x B is preferred Parameter limit specifies the limit for using AT x B multiplication, when nn=2. (It has no meaning for nn=1.) If size(A)/size(B) 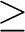 limit - standard multiplication is performed, limit - standard multiplication is performed,
size(A)/size(B) < limit - transposed multiplication is performed. (size(A,B) - number of elements in matrix A,B). Recommended value for limit is 2-3. Using of transposed matrix (nn=2) multiplication may bring some computer time reduction only in special cases, however, it requires some additional work space. Default is optimal for absolute majority of cases. This keyword is optional. (Default=1). |
Note, that CCSD and CCT keywords are mutually exclusive.
8.5.4 How to run closed shell calculations using ROHF CC codes
First of all it should be noted here, that it is not advantageous to run closed shell calculations using ROHF CC codes, since in the present implementation it will require the same number of arithmetical operations and the core and disk space like corresponding open shell calculations.
Since ROHF CC codes are connected to the output of RASSCF code (through the JOBIPH file), it is necessary to run closed shell Hartree-Fock using the RASSCF program. This can be done by setting the number of active orbitals and electrons to zero (also by including only doubly occupied orbitals into the active space; this has no advantage but increases the computational effort). to guarantee the single reference character of the wave function.
The CC program will recognize the closed shell case automatically and will reorganize all integrals in a required form. For more information the reader is referred to the tutorials and examples manual.
Below is an input file for HF+ CCSD(T) calculation.
&CCSDT
Title
HF(+) CCSD(T) input example
CCT
Triples
3
Next: 8.6 chcc Up: 8. Programs Previous: 8.4 casvb


 even in the case where the reference function
even in the case where the reference function
 is the proper
spin eigenfunction. The way how to reduce the spin
contamination and mainly the number of independent amplitudes is to introduce
the spin adaptation.
Besides the standard nonadapted (spinorbital) CCSD procedure this program
allows to use different levels of spin
adaptation of CCSD amplitudes (the recommended citations are Refs.
[
is the proper
spin eigenfunction. The way how to reduce the spin
contamination and mainly the number of independent amplitudes is to introduce
the spin adaptation.
Besides the standard nonadapted (spinorbital) CCSD procedure this program
allows to use different levels of spin
adaptation of CCSD amplitudes (the recommended citations are Refs.
[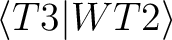 term. Second possibility represents the well known
extension to the first one by the
term. Second possibility represents the well known
extension to the first one by the
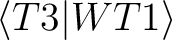 term
(W is the two electron perturbation). For closed shell
systems this is the most popular and most frequently used noniterative triples
method. For single determinant open shell systems, described by the
ROHF reference
function standard (Raghavachari et. al.) method needs to be extended by the
additional fourth order energy term, namely
term
(W is the two electron perturbation). For closed shell
systems this is the most popular and most frequently used noniterative triples
method. For single determinant open shell systems, described by the
ROHF reference
function standard (Raghavachari et. al.) method needs to be extended by the
additional fourth order energy term, namely
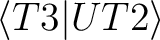 (U is the off-diagonal part of the Fock operator).
(U is the off-diagonal part of the Fock operator).